Many companies face difficulty to choose the right storage services that would match their goals as the cloud market offers numerous solutions for any business needs. In this article, we’d like to focus on S3, EBS, and EFS, as they belong to the persistent data storage type, which means that data there is durable and sticks around after reboots, restarts, or power cycles.

Additionally, according to AllCode, an Amazon Web Services Consulting Partner, Amazon Elastic File System (EFS), Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS), and Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) are included in the list of the most popular AWS services.
So, let’s consider the advantageous features of all three storage services, as well as discover their use cases to know which solution can be helpful for your organization in particular.
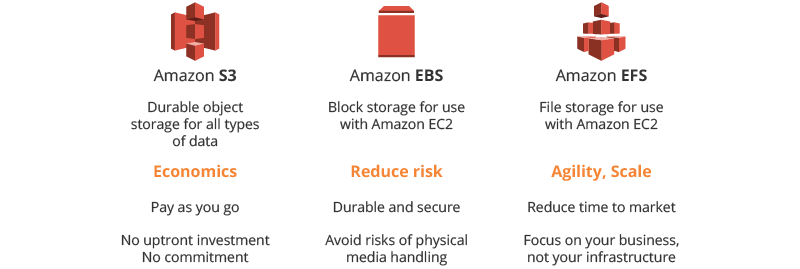
Amazon S3
AWS Simple Storage Service (S3) is the most popular object storage among many organizations. Below you can discover the reasons for such popularity.
S3 benefits
- Durability, scalability, and availability. Amazon S3 offers scaling of the storage resources for free. It protects your data from various threats, errors, and downtimes. This, in turn, makes your data accessible anytime you need it.
- High level of data protection. S3 follows the security and compliance standards. It means you can store data and consider it protected from unauthorized access due to proper encryption and access management tools. S3 is the only object storage service that has a Block Public Access feature that gives you the opportunity to block public access to all of your objects at the bucket. Additionally, AWS supports various auditing capabilities that allow you to monitor access requests to S3 resources.
- Cost-saving opportunities. There are several factors that influence S3 cost like the region where you store your data, the volume of stored data, the chosen S3 storage class, and so on. If you’re aware of them, you can optimize your S3 expenditures.
S3 use cases
- Backup and restoration. S3 can be combined with the other types of AWS storage like EBS and EFS to achieve secure backups and restoration. These offerings can help you meet compliance, recovery time, and recovery point objectives.
- Trustworthy disaster recovery. S3 storage provides the replication of sensitive data and mission-critical applications. It offers protection of resources by means of recovering data from different issues caused by a system failure or a natural disaster.
- Possibility to archive data. S3 offers archiving capabilities such as S3 Glacier and S3 Glacier Deep Archive. These services give users the opportunity to archive the less used data and store it for extended periods of time at their lowest rates. The main advantage is that S3 Glacier allows restoring any archived object within several minutes.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
Amazon EBS provides block storage volumes for use with EC2 instances. EBS volumes are attached to EC2s in the same way as the local disk drive is attached to the physical machine.
EBS benefits
- High availability and security. EBS volumes offer automatic replication within the Availability Zones these volumes are located. Security is provided by access control and encryption policies.
- Data backup and restoration. You can protect your data by backing up the EBS volumes to Amazon S3 with the help of taking real-time snapshots. They are incremental backups but cannot serve as a replacement for backup software. Here’s why: only the blocks on the device that have changed after your last snapshot are saved in the new snapshot. This minimizes the snapshots creation time and saves money by not duplicating data.
- Geographic diversity. EBS volume snapshots can be duplicated and resources can be placed in different locations to facilitate disaster recovery and data center migration. It’s useful in the case when the company’s client base is spread all around the world.
- Facilitated scalability. EBS volumes are scalable, so you can easily scale them both up and down. As it happens at a high speed, you get the required performance and needed capacity for changing computing needs.
- Potential cost savings. EBS requires upfront disk pre-allocation, so if you’ve performed a sophisticated pre-analysis and identified how much space you need to reach your goals, you can save a lot of money. This analytical work needs to be done, as EBS costs about a third as much as EFS per GB.
EBS use cases
- Testing and development. EBS perfectly suits development and testing aims, as this type of storage gives the opportunity to quickly and easily scale, duplicate, and archive the required environments.
- Relational databases. As EBS scales to meet changing storage needs, it’s a great choice for deploying relational databases, including PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, or Microsoft SQL Server. Depending on the amount of storage requested, Amazon RDS automatically stripes across multiple Amazon EBS volumes to enhance performance.
- International market. You can copy EBS Snapshots and AMIs to run apps in various AWS regions. Not only does it minimize the data loss, but it also increases the speed of recovery time due to regular data backups.
- Enterprise-wide applications. EBS is the powerful block storage that is enough to support essential applications (for instance, Microsoft SharePoint or Microsoft Exchange).
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS)
EFS is considered to be the best solution for the constantly fluctuating workloads, as it can scale automatically to meet the demand, no matter how rapidly it increases. What’s more important, EFS will automatically scale back down, when the demand spike decreases.
You can integrate EFS with different AWS services and access this type of AWS storage from all your instances. Let’s explore its advantages in detail.
EFS benefits
- Scalable performance. EFS can support any workload, no matter how rapidly your file system grows. It’s all due to automatical up and downscaling capability. Additionally, with EFS you don’t need to provision the storage preliminarily before adding any files.
- Constant accessibility. EFS ensures the possibility for EC2 instances and on-premises software to access the shared files anytime. Also, EC2 instances can access EFS file systems located in other AWS regions with the help of Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) peering.
- Service management. EFS is a complete managed service. This means that the company’s executives or even IT department teams don’t need to maintain the file system themselves, which saves time and frees employees to perform other tasks.
- Cost savings. EFS the most outstanding advantage is that you pay only for the storage you’re actually using. However, its cost is significant, especially when compared with the EBS cost.
- Reliable security and compliance. You can control access to your EFS file systems with the use of AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) or Amazon VPC permissions. EFS encrypts the data, even the one that is in transit, that provides trustworthy security and facilitates regulatory compliance.
EFS use cases
- Big data analytics. EFS is suitable for running applications with big data, that require low-latency file access, as well as demands significant throughput.
- Content management system and web server support. EFS is a solid file system that enables content management systems and supports web serving applications, such as websites and archives.
- Development of apps and testing. EFS is the only type of storage that delivers a shared file system that is necessary for sharing code and files across numerous computing resources.
Manage your storage
When deciding what type of Amazon storage to use (EBS, EFS, or S3), it’s better to consider all the details: advantages, the situation when you may need particular storage, as well as possible issues that may occur, like overspending or various security threats. Also, you may use all the above-mentioned storage types in order to meet all your business needs, instead of choosing one and only.
No matter what type of storage you’re deploying, keep in mind that cloud resources and costs should be properly managed. With Binadox you can view the utilization and cost rates for all S3, EFS, and EBS. Based on these rates the system forms recommendations that you can consider for optimizing AWS storage services.
To find out more about Binadox cost-saving practices sign up for a free 14-day trial period.

