Unleashing the Power of Cloud Technologies: The Influence of Shadow Organizations on Your Infrastructure
In the ever-evolving world of technology, cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing the way businesses operate and individuals access data. As the demand for seamless connectivity and on-demand resources continues to soar, understanding the fundamentals of cloud technologies has become paramount. However, alongside the rapid adoption of cloud computing, a phenomenon known as “shadow organizations” has emerged, posing potential challenges to organizations’ cloud infrastructure.
Shadow organizations refer to the unauthorized or unmanaged use of cloud services by individuals or teams within an organization, often without the knowledge or approval of the IT department. These shadow organizations arise when employees seek to leverage the convenience and flexibility of cloud technologies to meet their specific needs, circumventing established protocols and processes.
While the intention behind shadow organizations is often innocent, driven by a desire for efficiency and productivity, their existence can introduce significant risks to an organization’s security, compliance, and governance. Uncontrolled cloud usage can lead to data breaches, regulatory violations, and unmanaged costs, undermining the very benefits that cloud computing promises.
This article delves into the intricacies of cloud computing, exploring its core concepts, benefits, and the latest advancements in this dynamic field.
Additionally, it sheds light on the phenomenon of shadow organizations, examining their implications, and offering insights into strategies for managing and mitigating the associated risks. Moreover, you’ll learn what a canned report is, and its difference from other reports by reading this article.
By understanding both the opportunities and challenges presented by cloud technologies and shadow organizations, businesses can better navigate the complex landscape and unlock the full potential of these transformative technologies.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a paradigm shift in how we access and utilize computing resources. Instead of relying on local hardware and software installations, cloud technologies enable users to access a shared pool of computing resources, including storage, processing power, and applications, over the internet. These resources are hosted and managed by cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing services can be broadly categorized into three main categories:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS providers offer virtualized computing resources, including servers, storage, and networking capabilities, on a pay-as-you-go basis. Examples: Amazon EC2, and Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS delivers a complete development and deployment environment, including operating systems, databases, and programming languages. Developers can build and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. Examples: Google App Engine, Heroku.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS provides access to fully-fledged applications over the Internet, eliminating the need for local installations. Users can access these applications through web browsers or dedicated clients. Examples: Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Embracing cloud technologies offers numerous advantages for businesses and individuals alike:
1. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud solutions allow for rapid scaling of resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency. Organizations can easily scale up or down, avoiding the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.
2. Cost Optimization
By leveraging cloud technologies, businesses can significantly reduce operational costs associated with maintaining physical infrastructure. They only pay for the resources they consume, leading to substantial cost savings, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises.
3. Increased Collaboration and Accessibility
Cloud-based applications and data storage enable seamless collaboration among teams, regardless of their geographical location. Employees can access and share files, documents, and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering productivity and collaboration.
Cloud Cost Management and Optimization
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud technologies, effectively managing and optimizing cloud costs has become a critical aspect. Cloud cost management tools and strategies help organizations gain visibility into their cloud spending, identify areas for optimization, and implement cost-saving measures.
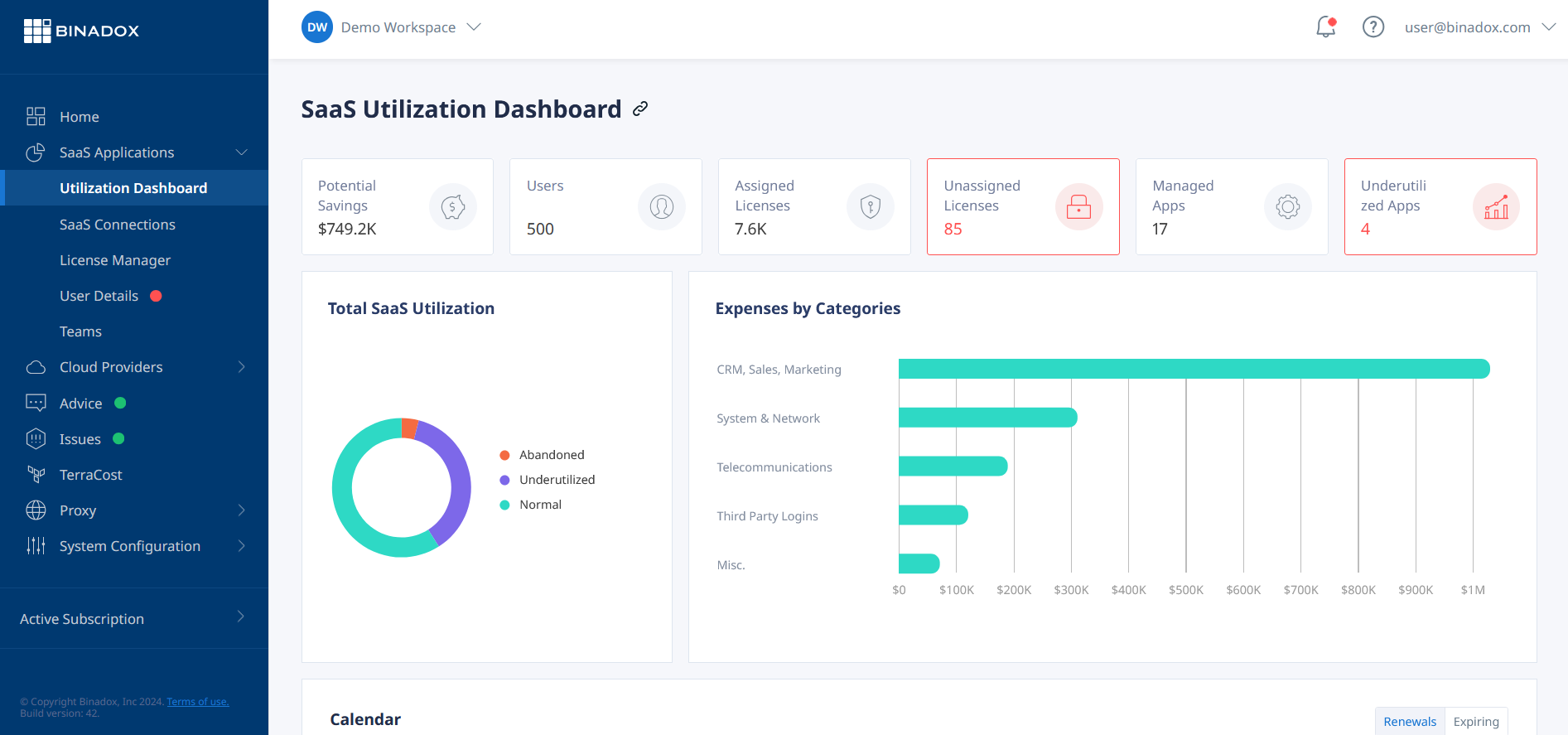
As you begin your cloud cost management journey, you’ll need to at least understand how to create a canned report. You’ll immediately notice the cost savings and see at a glance how much you’re spending on your entire cloud infrastructure.
Canned reports are pre-built, standardized reports that provide insights into various aspects of cloud resource utilization, costs, and performance. These reports offer a comprehensive view of an organization’s cloud footprint, enabling better decision-making and cost optimization.
Note:
If you want to learn how to maximize efficiency in software subscriptions, you can read our comprehensive guide SaaS Spend Management: Maximizing Efficiency in Software Subscriptions. This article delves into proven strategies for optimizing your SaaS spending, from identifying unused licenses to negotiating better deals with vendors. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, mastering SaaS spend management is essential for controlling costs and maximizing the value of your software investments.
What is a Canned Report?
Canned reports are typically offered by cloud cost management platforms or directly by cloud service providers. They are designed to address common use cases and provide actionable insights without the need for extensive customization or data analysis skills. Canned reports can cover a wide range of areas, including:
- Cost Breakdown: Canned reports that categorize cloud costs by service, project, department, or other relevant dimensions, allowing organizations to identify their biggest cost drivers.
- Resource Utilization: Canned reports that analyze the utilization of cloud resources, such as compute instances, storage, and databases, helping to identify underutilized or overprovisioned resources.
- Cost Forecasting: Predictive reports that estimate future cloud costs based on historical usage patterns and projected growth, enabling better budgeting and capacity planning.
- Cost Anomaly Detection: Canned reports that highlight unusual spikes or dips in cloud spending, alerting organizations to potential cost overruns or opportunities for optimization.
- Reserved Instance (RI) Analysis: For cloud providers that offer reserved instances, these canned reports analyze the organization’s RI usage and provide recommendations for optimizing RI purchases.
- Cost Allocation: Reports that facilitate cost allocation and chargeback across different departments, projects, or cost centers, ensuring accurate billing and accountability.
Benefits of Canned Reports
Canned reports offer several advantages for organizations seeking to optimize their cloud costs:
- Time-Saving: Pre-built reports eliminate the need for manual data analysis and report creation, saving valuable time and resources.
- Consistency and Standardization: Canned reports follow established best practices and industry standards, ensuring consistent and reliable data across the organization.
- Comprehensive Visibility: By providing a holistic view of cloud resource usage and costs, canned reports enable organizations to identify optimization opportunities they may have missed otherwise.
- Ease of Use: Canned reports are designed for easy consumption, often featuring intuitive dashboards and visualizations that make data interpretation straightforward.
- Scalability: As an organization’s cloud footprint grows, canned reports can scale accordingly, providing insights into complex cloud environments without additional effort.
Customization and Advanced Reporting
While canned reports offer a solid foundation for cloud cost management, organizations may require additional customization and advanced reporting capabilities to address their specific needs. Many cloud cost management platforms allow for the creation of custom reports, enabling organizations to tailor the data and visualizations to their unique requirements. Advanced reporting features may include:
- Ad-hoc Query and Analysis: The ability to perform on-the-fly querying and analysis of cloud cost data, enabling users to explore and uncover insights beyond pre-built reports.
- Data Integration: The capability to integrate cloud cost data with other data sources, such as business intelligence tools or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, for more comprehensive analysis and reporting.
- Automation and Scheduling: The ability to automate the generation and distribution of reports, ensuring stakeholders receive relevant information on a regular schedule.
- Collaborative Reporting: Features that enable teams to share, annotate, and collaborate on reports, fostering better communication and decision-making.
By leveraging both canned reports and advanced reporting capabilities, organizations can strike a balance between quick insights and in-depth analysis, enabling more effective cloud cost management and optimization strategies.
(Source: Binadox Blog, binadox.com/blog/)
The Rise of Shadow IT and Shadow Organizations
Let’s shift our focus from the topic of canned reports to a more challenging issue to tackle: the shadow IT phenomenon. With the proliferation of cloud technologies, a new phenomenon known as “shadow IT” has emerged.
Shadow IT refers to the unauthorized use of cloud services, applications, or resources by individuals or departments within an organization, often without the knowledge or approval of the IT department. This practice can lead to significant security risks, compliance issues, and uncontrolled cloud spending.
The rise of shadow IT is primarily driven by the ease of access and adoption of cloud services. Employees, seeking to streamline their workflows or leverage powerful cloud-based tools, may bypass official IT channels and independently procure and use cloud solutions. While this approach may offer short-term benefits, it can have far-reaching consequences for the organization.
Note:
We have discussed Shadow IT previously. You can delve deeper into this topic in the following article: Shadow IT: Risks and Benefits.
Risks Associated with Shadow IT
- Security Vulnerabilities | When cloud services are used without proper vetting and oversight, sensitive data may be exposed to unauthorized access, increasing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Compliance Violations | Many industries have strict regulations governing data handling and storage. Shadow IT can lead to non-compliance with these regulations, resulting in hefty fines and legal repercussions.
- Lack of Governance and Control | Unmanaged cloud resources can lead to redundancies, inefficiencies, and increased costs due to a lack of centralized governance and control.
- Integration Challenges | Shadow IT solutions may not integrate seamlessly with the organization’s existing systems and processes, hindering data sharing and collaboration.
- Vendor Management Issues | Without proper vendor management practices, organizations may find themselves dealing with multiple cloud service providers, making it challenging to negotiate favorable terms and maintain consistent security and compliance standards.
Embracing Shadow Organizations
To mitigate the risks associated with shadow IT, organizations are increasingly adopting a new approach called “shadow organizations.” These dedicated teams or departments are tasked with overseeing and governing the use of cloud resources within the organization, ensuring proper security, compliance, and cost optimization measures are in place. Shadow organizations typically consist of a cross-functional team representing various stakeholders, including IT, finance, legal, and business units. Their primary responsibilities include:
- Cloud Service Discovery | Identifying and cataloging all cloud services and resources being used across the organization, both sanctioned and unsanctioned.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation | Evaluating the risks associated with each cloud service, implementing appropriate security controls, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
- Vendor Management | Establishing vendor relationships, negotiating favorable terms, and ensuring consistent security and compliance standards across all cloud service providers.
- Policy Development and Enforcement | Developing and enforcing policies and guidelines for the appropriate use of cloud services, including procurement processes, access controls, and data handling procedures.
- Cost Optimization | Monitoring and optimizing cloud spending by identifying redundancies, rightsizing resources, and implementing cost-saving strategies.
- Training and Awareness | Educating employees about the risks of shadow IT and promoting the use of approved and secure cloud services.
By establishing shadow organizations, companies can strike a balance between empowering employees with the agility and flexibility of cloud technologies while maintaining centralized control, security, and compliance.
Best Practices for Managing Shadow IT
To effectively manage shadow IT and leverage the benefits of shadow organizations, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Foster Open Communication | Encourage open communication between IT departments and business units to understand the needs and pain points driving shadow IT adoption.
- Streamline Procurement Processes | Implement streamlined processes for evaluating, approving, and procuring cloud services, reducing the temptation for employees to bypass official channels.
- Continuous Monitoring and Auditing | Regularly monitor and audit cloud resource usage to identify instances of shadow IT and take appropriate actions.
- Embrace Agility and Innovation | Empower shadow organizations to rapidly evaluate and adopt new cloud technologies that can drive business value while maintaining proper governance and control.
- Leverage Automation and AI | Utilize automation and artificial intelligence tools to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and optimize cloud resource usage, reducing the risk of shadow IT proliferation.
By proactively addressing the challenges posed by shadow IT and implementing effective governance strategies through shadow organizations, businesses can harness the full potential of cloud technologies while mitigating risks and maximizing the return on their cloud investments.
Note:
Forbes has also written on how to embrace shadow organizations. You can learn more about it here: Don’t Fear Shadow IT: Embrace It.
Cloud Security and Compliance
While cloud technologies offer numerous benefits, security and compliance remain critical considerations. As organizations entrust their valuable data and workloads to cloud service providers, ensuring the protection of sensitive information and adhering to relevant industry regulations and standards is paramount.
Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud security is based on a shared responsibility model, where the cloud service provider and the customer share the burden of securing the cloud environment. The cloud provider is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, including physical data centers, network, and virtualization layers. Customers, on the other hand, are responsible for securing their applications, data, operating systems, and access management within the cloud environment.
This shared responsibility model requires close collaboration and a clear delineation of responsibilities between the provider and the customer. By understanding their respective roles and implementing appropriate security controls, organizations can effectively mitigate risks and maintain a robust security posture in the cloud.
Cloud Security Measures
Cloud service providers implement robust security measures to protect their customers’ data and resources. These measures typically include:
- Data Encryption | Both data at rest (stored data) and data in transit (data being transmitted) are encrypted using industry-standard encryption protocols to prevent unauthorized access.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) | IAM controls govern who can access cloud resources and what actions they can perform, ensuring proper access control and segregation of duties.
- Network Security | Virtual private clouds (VPCs), firewalls, and other network security controls are implemented to isolate and protect customer environments from external threats.
- Physical Security | Cloud data centers are secured with state-of-the-art physical security measures, such as biometric access controls, surveillance systems, and environmental monitoring.
- Regular Security Updates | Cloud providers continuously monitor for security vulnerabilities and promptly release updates and patches to address any identified risks.
- Compliance Certifications | Major cloud providers obtain and maintain compliance certifications for various industry standards and regulations, such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, ISO 27001, and SOC 2, to assure customers of their adherence to security best practices.
Customer Responsibilities
While cloud service providers implement robust security measures, customers also play a crucial role in securing their cloud environments. Key responsibilities for customers include:
- Data Classification and Encryption | Classifying and appropriately encrypting sensitive data to ensure proper protection and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Access Controls | Implementing strong access controls, such as multi-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing and revoking unnecessary access privileges.
- Configuration Management | Ensuring that cloud resources are configured securely and following best practices for hardening and patching.
- Security Monitoring and Logging | Continuously monitoring cloud environments for potential threats and maintaining comprehensive logs for auditing and incident response.
- Compliance Adherence | Understanding and adhering to relevant industry regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, and implementing appropriate security controls to maintain compliance.
- Incident Response Planning | Developing and testing incident response plans to effectively respond to and mitigate potential security breaches or incidents.
Emerging Security Challenges and Solutions
As cloud adoption continues to grow and threat landscapes evolve, new security challenges emerge. These challenges include:
Distributed Cloud Environments
With the rise of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, securing and maintaining visibility across distributed cloud environments becomes increasingly complex.
Insider Threats
Malicious insiders or compromised accounts can pose significant risks to cloud environments, highlighting the need for robust access controls and monitoring.
Automated Threats
Sophisticated automated threats, such as botnets and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, require advanced detection and mitigation techniques. To address these challenges, cloud service providers and security vendors are developing advanced solutions, such as:
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): CSPM tools provide continuous monitoring, assessment, and remediation of cloud security configurations and compliance across multiple cloud environments.
- Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP): CWPPs offer comprehensive security solutions for protecting cloud workloads, including virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB): CASBs act as intermediaries between users and cloud services, enforcing security policies, monitoring activities, and protecting against threats.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML are being leveraged to detect and respond to advanced threats, anomalies, and suspicious behavior in cloud environments.
By embracing a proactive and collaborative approach to cloud security, organizations can reap the benefits of cloud technologies while maintaining robust security postures and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
(Source: AWS Cloud Pages, pages.awscloud.com)
The Future of Cloud Computing
The cloud computing landscape is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for innovative solutions. As we look to the future, several trends and developments are poised to shape the next generation of cloud technologies.
Edge Computing and the Internet of Things (IoT)
Edge computing brings computing resources closer to the data source, enabling faster processing and reduced latency, which is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles, real-time analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT). By processing data at the edge, rather than sending it to a centralized cloud, edge computing reduces network congestion and improves response times, which is particularly important for time-sensitive applications.
The proliferation of IoT devices, ranging from wearables to industrial sensors, is driving the demand for edge computing capabilities. These devices generate vast amounts of data that need to be processed and analyzed in real-time, making traditional cloud computing architectures less efficient. Edge computing solutions, combined with advanced analytics and machine learning, will play a pivotal role in unlocking the full potential of IoT across various industries.
Serverless Computing and Function-as-a-Service (FaaS)
Serverless computing, also known as Function-as-a-Service (FaaS), represents a paradigm shift in application development and deployment. With serverless computing, developers no longer need to manage server infrastructure or worry about provisioning and scaling resources. Instead, they write and deploy individual functions or pieces of code that are executed in response to specific events or triggers.
The serverless approach offers several advantages, including reduced operational overhead, automatic scaling, and a pay-per-use pricing model, making it highly cost-effective for event-driven applications and microservices architectures. Major cloud providers, such as AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Azure Functions, are driving the adoption of serverless computing, enabling developers to focus on writing code without worrying about infrastructure management.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
As organizations diversify their cloud needs and seek to mitigate vendor lock-in risks, hybrid and multi-cloud strategies are becoming increasingly prevalent. A hybrid cloud approach combines on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both environments. This approach is particularly attractive for organizations with strict regulatory requirements, legacy systems, or workloads that require low-latency access to on-premises resources.
Multi-cloud strategies, on the other hand, involve the use of multiple public cloud providers, each offering unique capabilities and services. By leveraging multiple cloud providers, organizations can optimize their workloads based on specific requirements, such as performance, pricing, or geographical location. However, managing a multi-cloud environment introduces complexities in areas like data integration, security, and cost management, driving the need for robust multi-cloud management tools and strategies.
Note:
Binadox also explored the comparison between the hybrid and multi-cloud approaches to infrastructure creation. For further insights, you can read about it here: Hybrid Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud .
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in the Cloud
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities into cloud platforms is poised to transform various industries and applications. Cloud providers are investing heavily in AI and ML services, offering pre-built models, development tools, and scalable compute resources for training and deploying AI models.
By leveraging cloud-based AI and ML services, organizations can accelerate their AI initiatives without the need for substantial upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure. These services enable rapid experimentation, prototyping, and deployment of AI-powered applications, such as natural language processing, computer vision, predictive analytics, and recommendation systems.
Moreover, the combination of AI and cloud computing can drive automation and optimization across various domains, including cloud resource management, cybersecurity, and customer experience optimization.
Sustainable and Green Cloud Computing
As environmental concerns grow, the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly cloud computing solutions is increasing. Major cloud providers are investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to power their data centers and reduce their carbon footprint.
Additionally, they are implementing energy-efficient cooling systems, optimizing resource utilization, and developing innovative technologies to minimize the environmental impact of their operations.
Furthermore, cloud computing itself can contribute to sustainability by enabling resource sharing and reducing the need for on-premises infrastructure, leading to lower energy consumption and decreased e-waste. However, as cloud adoption continues to grow, it is crucial for providers and organizations to prioritize sustainable practices and embrace green computing initiatives.
Quantum Computing in the Cloud
Quantum computing, which harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations exponentially faster than classical computers, is a rapidly emerging field with significant potential. While still in its early stages, quantum computing promises to revolutionize various domains, including cryptography, drug discovery, financial modeling, and scientific simulations.
Cloud providers are already exploring the integration of quantum computing capabilities into their platforms, enabling researchers, scientists, and developers to access and experiment with quantum computing resources on demand. As quantum computing matures and becomes more accessible through the cloud, it could open up new frontiers in problem-solving and enable breakthroughs in areas previously thought impossible with classical computing.
Conclusion
Cloud technologies have transformed the way we access, store, and process data, enabling unprecedented levels of scalability, collaboration, and cost optimization. As organizations continue to embrace cloud computing, it is crucial to understand the fundamentals, leverage best practices for cloud cost management, and stay abreast of the latest developments in this rapidly evolving field.
Binadox plays a crucial role in supporting organizations by providing comprehensive cloud cost management and optimization solutions. Through Binadox, organizations can discover and catalog all cloud resources, including unsanctioned shadow IT deployments, enabling effective governance and risk assessment.
Binadox empowers organizations to monitor and optimize cloud spending across the organization, identify redundancies and cost-saving opportunities, and enforce policies and guidelines for appropriate cloud service usage.
With Binadox’s pre-built canned reports, advanced analytics, and integration capabilities, gain comprehensive insights into cloud resource utilization, costs, and performance, enabling data-driven decision-making and proactive risk mitigation.
Additionally, Binadox’s automation, scheduling, and collaborative reporting features streamline processes, enhance transparency, and foster better communication within organizations.
By leveraging Binadox’s capabilities, organizations can effectively govern and manage shadow IT resources while unlocking the benefits of cloud technologies for the entire organization.

