
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the Internet of Things (IoT) devices have become an integral part of our daily lives. From smart home appliances to industrial machinery, these devices generate vast amounts of data and require efficient management throughout their lifecycles. As we approach 2024, the need for robust Device Lifecycle Management (DLM) solutions has become increasingly crucial.
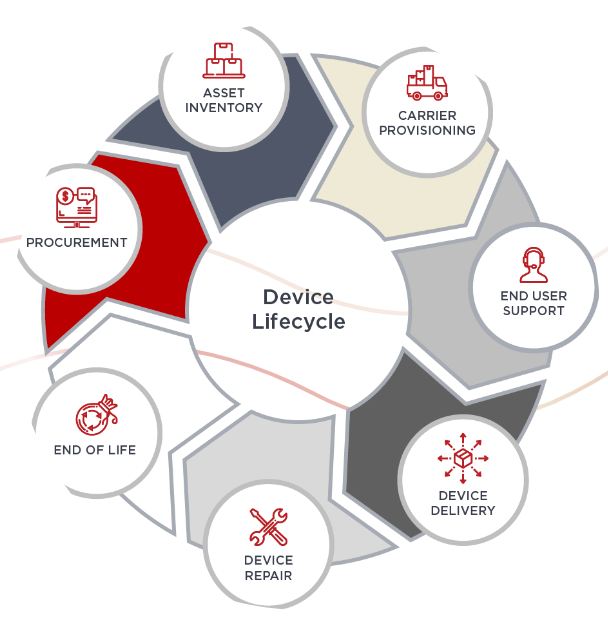
DLM refers to the process of managing IoT devices from their initial deployment to eventual decommissioning. It encompasses various stages, including provisioning, monitoring, maintenance, and retiring devices. Effective DLM strategies ensure optimal device performance, security, and cost-effectiveness, ultimately contributing to a seamless user experience.
What is Device Lifecycle Management?
Device Lifecycle Management (DLM) is a comprehensive approach to managing IoT devices from their initial deployment to eventual decommissioning. It encompasses various stages, including provisioning, monitoring, maintenance, updates, and retiring devices. Effective DLM strategies ensure optimal device performance, security, and cost-effectiveness, ultimately contributing to a seamless user experience and maximizing the value derived from IoT investments.
The Importance of Device Lifecycle Management
In the era of the Internet of Things, organizations face numerous challenges when it comes to managing their connected devices. These challenges include:
- Device Proliferation: The rapid growth in the number of IoT devices makes manual management increasingly complex and time-consuming.
- Security Risks: Unmanaged devices can pose significant security risks, leaving organizations vulnerable to cyber threats such as data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Compliance Requirements: Various industries have specific regulations and standards that must be adhered to throughout the device lifecycle.
- Cost Management: Inefficient device management can lead to unnecessary costs due to resource wastage, downtime, and security incidents.
By implementing effective DLM strategies, organizations can address these challenges, ensuring optimal device performance, enhanced security, compliance with industry regulations, and cost savings.
Benefits of Device Lifecycle Management
Implementing an effective device lifecycle management (DLM) strategy offers numerous benefits, ensuring efficient utilization of resources, enhanced security, and streamlined operations throughout the lifecycle of devices.
Cost Optimization
One of the primary benefits is cost optimization. DLM facilitates cost savings through precise planning for device lifespans, allowing for informed budgeting and preventing unforeseen costs during transitions. It enables resource optimization by maintaining a vigilant inventory, monitoring usage patterns, and eliminating unnecessary expenditures.
Additionally, device lifecycle management empowers organizations with comprehensive data on device requirements and replacement schedules, strengthening their position in vendor negotiations and leading to favorable terms and substantial cost savings.
Robust Security
Another significant benefit of device lifecycle management is robust security. DLM enhances security by ensuring devices receive timely security updates, fortifying them against evolving threats and maintaining a robust digital environment. Its centralized monitoring capabilities facilitate swift detection of anomalies or security breaches, triggering rapid response mechanisms to minimize operational disruption.
By employing state-of-the-art encryption protocols and strict access controls, DLM safeguards sensitive data from creation to disposal, ensuring only authorized personnel can access critical information.
Compliance Assurance
Device lifecycle management also plays a crucial role in compliance assurance. It enables organizations to rigorously enforce and monitor security policies, minimizing non-compliance risks and ensuring adherence to industry regulations. It provides transparent data access visibility, showcasing adherence to robust data handling practices and instilling trust among stakeholders and regulatory bodies.
Additionally, device lifecycle management guarantees compliance with regulations during device retirement, including thorough data wiping to prevent breaches, exemplifying commitment to both data security and environmental responsibility.
Operational Continuity
Furthermore, device lifecycle management contributes to operational continuity. It reduces downtime through proactive maintenance schedules and timely upgrades, preventing device failures and ensuring uninterrupted business operations. Its innovative system empowers IT teams to preemptively identify and address potential device issues, drastically reducing downtime and maintaining consistently high levels of employee productivity.
Furthermore, DLM streamlines the onboarding process, ensuring new employees receive properly configured devices promptly, minimizing disruption and fostering quick integration into the workforce.
Enhanced Employee Experience
Finally, device lifecycle management plays a vital role in enhancing the employee experience. By providing reliable and optimized devices, DLM enables uninterrupted productivity, minimizing disruptions and significantly boosting employee efficiency. It empowers seamless collaboration, fostering an environment where ideas flow freely, and teamwork is optimized.
Equipping employees with dependable devices enhances job satisfaction, contributes to a positive work atmosphere, and boosts confidence, ultimately encouraging innovation and the pursuit of new ideas.
Types of Device Lifecycle Management
Device lifecycle management can be categorized into two main types: on-premises and cloud-based.
- On-premises DLM solutions involve deploying and managing the DLM infrastructure within an organization’s own data centers or servers. This approach offers greater control and customization, but requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
- Cloud-based DLM solutions, on the other hand, leverage the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing, enabling organizations to manage their devices through a centralized, cloud-based platform. Cloud-based DLM is often more cost-effective, scalable, and easier to maintain, making it an attractive option for many organizations.
Device lifecycle management refers to the process of managing IoT devices from their initial deployment to eventual decommissioning. It encompasses various stages, including provisioning, monitoring, maintenance, and retiring devices.
Effective device lifecycle management strategies ensure optimal device performance, security, and cost-effectiveness, ultimately contributing to a seamless user experience.
Cloud Technologies in Device Lifecycle Management
Cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of DLM, offering scalable and flexible solutions for managing IoT devices. Cloud-based device lifecycle management platforms provide a centralized hub for device management, enabling organizations to monitor, control, and maintain their devices from a single interface. These platforms leverage the power of cloud computing to deliver advanced features and capabilities, including:
- Scalability: Cloud-based DLM solutions can easily scale up or down to accommodate fluctuating device numbers, ensuring efficient resource allocation and cost optimization.
- Remote Access: With cloud-based DLM, organizations can remotely access and manage their devices from anywhere, eliminating the need for on-site personnel and reducing operational costs.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Cloud-based platforms facilitate seamless OTA updates, ensuring that devices remain up-to-date with the latest software versions, security patches, and firmware upgrades.
- Data Analytics: By leveraging cloud computing’s data processing capabilities, organizations can gain valuable insights into device performance, usage patterns, and potential issues, enabling proactive maintenance and optimization.
- Security and Compliance: Cloud-based DLM solutions often incorporate robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and auditing capabilities, helping organizations maintain compliance with industry regulations and standards.
(Source: Binadox, binadox.com)
Key Stages of Device Lifecycle Management
Effective device lifecycle management involves several key stages, each playing a crucial role in ensuring efficient and secure device management. These stages include:
Provisioning and Deployment
The provisioning and deployment stage involves the initial setup and configuration of IoT devices. This stage encompasses activities such as device registration, software installation, and network connectivity setup. Cloud-based DLM solutions streamline this process by providing centralized device onboarding and automated provisioning capabilities.
Monitoring and Management
Once deployed, IoT devices require continuous monitoring and management to ensure optimal performance and identify potential issues. Cloud-based device lifecycle management platforms offer real-time device monitoring, allowing organizations to track device status, health, and usage patterns. These platforms also enable remote device management, such as configuring settings, updating software, and troubleshooting issues.
Maintenance and Updates
To maintain device functionality and security, regular maintenance and updates are essential. Cloud-based device lifecycle management solutions simplify this process by enabling OTA software and firmware updates, minimizing downtime and reducing the need for on-site maintenance. Additionally, these platforms often incorporate automated patch management capabilities, ensuring that devices remain up-to-date with the latest security patches and bug fixes.
Decommissioning and Retirement
At the end of an IoT device’s lifecycle, proper decommissioning and retirement procedures are crucial to ensure data security and compliance. Cloud-based DLM platforms streamline this process by providing centralized device retirement workflows, including data wiping, device deregistration, and secure disposal or repurposing.
Best Practices for Device Lifecycle Management
To maximize the benefits of device lifecycle management and ensure efficient device management, organizations should consider the following best practices:
Adopt a Structured Approach
Establish clear policies and procedures for each stage of the device lifecycle, from provisioning to decommissioning. This includes defining device onboarding processes, such as device registration, software installation, and network connectivity setup.
Outline update and maintenance schedules, specifying the frequency and processes for software updates, firmware upgrades, and preventive maintenance activities.
Develop comprehensive security protocols, covering access controls, encryption methods, and incident response procedures.
Additionally, create detailed decommissioning workflows that address data wiping, device deregistration, and secure disposal or repurposing of devices.
Prioritize Security
Implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments, to protect devices and data throughout the lifecycle. Conduct regular vulnerability assessments and promptly address identified risks.
Encrypt data in transit and at rest using industry-standard encryption protocols.
Implement role-based access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access and manage devices.
Regularly assess the security posture of your devices and device lifecycle management infrastructure, and promptly apply security patches and updates to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Integrate with Existing Systems
Ensure seamless integration between the device lifecycle management platform and existing IT infrastructure, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and identity and access management (IAM) systems. This integration facilitates data sharing, streamlines processes, and enhances overall efficiency.
For example, integrate the DLM platform with your organization’s IAM system to centralize user authentication and authorization, or connect it with your ERP system to synchronize device inventory and asset management data.
Foster Collaboration
Encourage cross-functional collaboration between IT, operations, security, and business teams to ensure a holistic approach to device lifecycle management. Regular communication and alignment between stakeholders can help identify potential issues and optimize processes.
Establish cross-functional teams or working groups dedicated to device lifecycle management, and encourage knowledge sharing and collaboration across departments. This collaborative approach can lead to better decision-making, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced risk management.
Monitor and Optimize
Continuously monitor device performance, usage patterns, and costs to identify areas for optimization and cost savings. Leverage data analytics and reporting capabilities to gain insights and make data-driven decisions.
Implement monitoring tools and dashboards to track key performance indicators (KPIs), such as device uptime, resource utilization, and operational costs. Analyze usage patterns to identify underutilized or redundant devices, and optimize resource allocation accordingly.
Implement Centralized Management
Adopt a centralized management approach to streamline device lifecycle operations. A centralized device lifecycle management platform provides a single pane of glass for managing devices, reducing complexity and enabling consistent policy enforcement.
With a centralized platform, you can easily provision, monitor, and manage devices from a unified interface, ensuring consistent application of security policies, software updates, and maintenance procedures across your entire device fleet.
Plan for Scalability
Ensure that your device lifecycle management solution is scalable and can accommodate future growth in the number of devices and data volumes. Cloud-based DLM platforms often offer better scalability compared to on-premises solutions.
Leverage the elasticity and auto-scaling capabilities of cloud computing to dynamically allocate resources based on changing device management demands.
Additionally, consider implementing a modular and extensible DLM architecture that can easily integrate with new technologies and accommodate future requirements.
Regularly Update and Maintain Devices
Establish processes for regularly updating and maintaining devices to ensure they remain secure, compliant, and performant. Leverage automation and over-the-air (OTA) update capabilities to streamline this process.
Define update schedules and testing procedures to minimize disruptions and ensure seamless deployment of software updates and firmware upgrades.
Implement preventive maintenance routines, such as diagnostic checks, performance tuning, and hardware inspections, to proactively identify and address potential issues.
Train and Educate Personnel
Invest in training and educating personnel involved in device lifecycle management. Ensure they understand the processes, tools, and best practices to effectively manage devices throughout their lifecycle.
Provide comprehensive training on the DLM platform, security protocols, and industry-specific regulations and standards. Encourage continuous learning and skill development to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in the field of DLM.
An Effective Device Lifecycle Management Strategy
As an organization embracing the Internet of Things (IoT) revolution, implementing a robust and comprehensive Device Lifecycle Management (DLM) strategy is crucial for maximizing the value of your connected devices while minimizing risks and operational challenges.
A well-designed device lifecycle management approach should seamlessly integrate various aspects of device management, from initial deployment to eventual decommissioning.
At the heart of your DLM strategy should be a centralized management platform that serves as a command center for all device-related activities. This platform, preferably cloud-based for scalability and remote access, will provide a unified interface for provisioning, monitoring, updating, and retiring devices across your organization.
Automating tasks such as device onboarding, software installations, and network configurations will streamline processes, reduce manual effort, and minimize errors.
Continuous monitoring of device status, health, and performance is paramount for proactive issue detection and resolution. Leverage real-time monitoring capabilities within your DLM platform to identify anomalies, security breaches, or potential issues promptly.
Empower your IT teams with remote device management functionalities, enabling them to troubleshoot, configure settings, and apply updates or patches from a centralized location.
Prioritizing security and compliance should be at the forefront of your DLM strategy. Implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments, to safeguard your devices and data throughout their lifecycle.
Ensure adherence to industry regulations and standards by enforcing security policies, maintaining transparent data access visibility, and implementing secure device retirement procedures.
Leverage over-the-air (OTA) update capabilities to streamline software and firmware updates across your connected devices. Establish automated update processes, including testing, staging, and rollout mechanisms, to ensure seamless and secure updates with minimal downtime.
Additionally, implement predictive maintenance strategies by analyzing device performance data and usage patterns, enabling proactive measures to prevent failures or downtime.
Continuously monitor device usage and resource consumption to identify opportunities for optimization. Decommission or repurpose underutilized or obsolete devices to reduce operational costs.
Leverage comprehensive device data to strengthen vendor negotiations and achieve cost savings. Foster cross-functional collaboration between IT, operations, security, and business teams to ensure a holistic approach to DLM, facilitating informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
Regularly assess and refine your DLM processes, policies, and tools based on feedback, performance metrics, and emerging best practices. Encourage continuous learning and skill development for personnel involved in DLM to stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and trends.
Incorporate advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and robotic process automation (RPA), to enhance DLM capabilities, automate repetitive tasks, identify patterns and anomalies, and optimize decision-making processes.
By adopting a comprehensive DLM strategy tailored to your organization’s needs, you can maximize the value derived from your IoT investments, ensure optimal device performance, enhance security and compliance, and achieve operational excellence throughout the device lifecycle.
The TOP-5 Device Lifecycle Management Tools
Microsoft Azure IoT Hub
Microsoft Azure IoT Hub is a cloud-based service that provides a comprehensive DLM solution for IoT devices. It enables device provisioning, monitoring, firmware updates, and secure communication between devices and cloud services.
IBM Watson IoT Platform
IBM Watson IoT Platform offers a complete DLM solution that includes device registration, software management, diagnostic data collection, and secure communication. It also provides advanced analytics and cognitive capabilities.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) IoT Core
AWS IoT Core is a managed cloud service that enables secure device connectivity and management. It supports device provisioning, software updates, data processing, and integration with other AWS services.
(Source: AWS Documentation, docs.aws.amazon.com)
Google Cloud IoT Core
Google Cloud IoT Core is a fully managed service that allows secure device connectivity and management. It offers device provisioning, software updates, data ingestion, and integration with other Google Cloud services.
PTC ThingWorx
PTC ThingWorx is an end-to-end IoT platform that includes DLM capabilities such as device provisioning, remote monitoring, software updates, and predictive maintenance. It also offers advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities.
These device lifecycle management tools provide a range of features and capabilities for managing IoT devices throughout their lifecycle. They enable device provisioning, monitoring, software updates, security, and integration with other systems and services. The choice of tool often depends on the specific requirements, existing infrastructure, and the IoT ecosystem being utilized by an organization.
Conclusion
As we navigate the rapidly evolving IoT landscape, effective Device Lifecycle Management (DLM) has become an essential component for organizations seeking to maximize the benefits of connected devices while mitigating risks and minimizing costs.
By leveraging cloud technologies, organizations can implement scalable and flexible DLM solutions, enabling centralized device management, remote access, seamless updates, and robust security measures.
Implementing best practices, such as adopting a structured approach, leveraging automation, prioritizing security, integrating with existing systems, fostering collaboration, and continuously monitoring and optimizing, organizations can achieve efficient device management throughout the entire lifecycle.
As we look ahead to 2024 and beyond, the growing complexity and proliferation of IoT devices will further emphasize the importance of robust device lifecycle management strategies. By embracing cloud-based DLM solutions and adhering to industry best practices, organizations can stay ahead of the curve, ensuring optimal device performance, enhanced security, and cost-effective operations.
To gain a deeper understanding of cloud technologies, visit the Binadox blog. This blog offers comprehensive insights and up-to-date information on various cloud computing topics.

