
In the ever-expanding world of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands as a titan, offering a vast array of services to businesses of all sizes. However, as companies increasingly rely on AWS for their infrastructure needs, many overlook a crucial aspect of cloud management: AWS data transfer charges. These fees, often hidden in the complexity of AWS pricing models, can significantly impact your bottom line if not properly understood and managed.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of AWS data transfer pricing, exploring everything from basic concepts to advanced optimization strategies. Whether you’re a startup just beginning your cloud journey or an enterprise looking to fine-tune your AWS expenses, understanding these AWS data transfer fees is key to maximizing the value of your cloud investment. We’ll unpack the various types of data transfer, demystify AWS data transfer pricing structures, and provide practical tips to help you navigate the sometimes confusing world of AWS data transfer charges.
Note:
Learn more about AWS Technologies in our other article What is Amazon Web Services (AWS) in Cloud Computing?.
What is AWS Data Transfer?
AWS data transfer refers to the movement of data into, out of, or between AWS services. This process is crucial for many cloud-based operations, but it can also impact your bill significantly. Understanding AWS data transfer fees is essential for effectively managing your cloud infrastructure and costs. This process is essential for various operations, including:
- Uploading files to S3 buckets
- Accessing EC2 instances
- Retrieving data from databases
- Serving content to end-users
Understanding these transfers is key to managing your AWS data transfer charges effectively.
(Source: AWS Blog, aws.amazon.com/blogs)
Importance of AWS Data Transfer
Data transfer is a fundamental aspect of cloud computing. It enables businesses to:
- Distribute content globally
- Backup and restore data
- Implement disaster recovery strategies
- Integrate various cloud services
- Perform data analysis across different systems
Measuring Data Transfer
AWS measures data transfer in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB). The amount of data transferred directly affects your AWS data transfer fees, making it crucial to monitor and optimize your data transfer patterns.
Data Transfer vs. Bandwidth
It’s important to distinguish between data transfer and bandwidth. While data transfer refers to the total amount of data moved over a period, bandwidth represents the maximum rate at which data can be transferred. AWS charges for data transfer, not bandwidth usage. This distinction is crucial for understanding AWS data transfer pricing.
Understanding these concepts is crucial for effectively managing your AWS infrastructure and optimizing costs. In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into how AWS applies AWS data transfer charges for different types of data transfer and explore strategies to minimize your AWS data transfer fees.
(Source: AWS Blog, aws.amazon.com/blogs)
AWS Data Transfer Charges Explained
Understanding AWS data transfer fees is essential for managing your cloud costs effectively. These AWS data transfer charges vary based on several factors and can significantly impact your overall AWS bill. Let’s dive deeper into how AWS structures its AWS data transfer pricing.
Factors Affecting AWS Data Transfer Pricing
- Direction of data transfer: Inbound vs. outbound traffic
- Volume of data transferred: Higher volumes often qualify for lower per-GB rates
- Source and destination regions: Transfers between different regions incur varying AWS data transfer fees
- Type of AWS services involved: Some services have specific AWS data transfer pricing models
The Complexity of AWS Data Transfer Pricing
AWS data transfer pricing can be complex due to its multi-faceted nature. It’s not just about how much data you’re moving, but also where it’s going and which services are involved. This complexity allows for fine-grained AWS data transfer charges but can also make cost estimation challenging.
Free Tier Considerations
AWS offers a Free Tier for many services, including some data transfer allowances. For example, new AWS accounts get 1 GB of free outbound data transfer each month for 12 months. It’s crucial to understand these free tier limits to avoid unexpected charges.
Data Transfer OUT vs. Data Transfer IN
A key principle of AWS pricing is that data transfer into AWS (ingress) is generally free, while data transfer out of AWS (egress) is charged. This model encourages users to bring data into the AWS ecosystem.
Regional Data Transfer Pricing
Data transfer costs can vary significantly between AWS regions. For instance, data transfer out of US regions is generally less expensive than out of South America or Asia Pacific regions. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for cost-effective global deployments.
Inter-Service Data Transfer
While data transfer between many AWS services within the same region is free, there are exceptions. For example, data transfer from Amazon EC2 to Amazon S3 in the same region is free, but transfer from EC2 to a different region’s S3 bucket would incur charges.
Data Transfer Acceleration Services
AWS offers services like S3 Transfer Acceleration and CloudFront to speed up data transfers. While these services can improve performance, they also come with their own pricing structures that need to be considered in your overall cost analysis.
(Source: Amazon Web Services, aws.amazon.com)
Note:
Learn what AWS S3 storage is, define what factors affect S3 pricing, as well as discover what classes of S3 storage can be deployed in our other article AWS S3 Pricing Explained.
Hidden Data Transfer Costs
Some AWS services may incur data transfer charges that aren’t immediately obvious. For instance, using AWS Lambda to process data in S3 can result in data transfer charges if the Lambda function and S3 bucket are in different regions.
Impact of Network Design on Costs
Your network architecture can significantly impact data transfer costs. For example, using a hub-and-spoke model with a central VPC peered to multiple other VPCs can lead to inter-availability Zone data transfer charges that might be avoidable with a different design.
Understanding these nuances of AWS data transfer pricing is crucial for accurate cost estimation and optimization. In the following sections, we’ll explore specific pricing details for different types of data transfer and discuss strategies to minimize these costs.
Types of Data Transfer
Inbound data transfer
This involves moving data from external sources into AWS services. For example, uploading files to Amazon S3 buckets or importing databases into Amazon RDS.
Inbound data transfer to most AWS services is typically free. This encourages users to move their data into the AWS ecosystem.
Example: Uploading 1TB of data from your on-premises server to an Amazon S3 bucket incurs no data transfer charges.
Outbound data transfer
This occurs when data is sent from AWS services to external destinations, such as delivering content to end-users or backing up data to on-premises systems.
AWS data transfer fees are primarily associated with outbound traffic. The pricing varies based on the total amount of data transferred out of AWS to the Internet.
Tiered Pricing Structure
- First 1GB per month: Free
- Up to 10TB per month: $0.09 per GB
- Next 40TB per month: $0.085 per GB
- Next 100TB per month: $0.07 per GB
- Over 150TB per month: Contact AWS for custom pricing
Inter-region data transfer
This involves moving data between different AWS regions, like transferring data from the US East (N. Virginia) to the EU (Ireland).
Moving data between different AWS regions incurs charges. These fees help cover the costs of AWS’s global network infrastructure.
Example: Transferring 100GB of data from the US East (N. Virginia) to the EU (Ireland) would cost approximately $2.00.
Intra-region data transfer
This refers to data movement within the same AWS region, such as between different Availability Zones or AWS services in the same region.
Data transfer within the same AWS region is generally free between most services. However, there are some exceptions.
Exceptions to Free Intra-Region Transfer
- Transfer between Availability Zones
- Transfer to and from Amazon CloudFront
Optimizing AWS Data Transfer Costs
Understanding AWS data transfer pricing allows you to implement strategies to reduce your cloud expenses. To minimize AWS data transfer charges, consider these strategies:
1. Use CloudFront for Content Delivery
Amazon CloudFront can reduce data transfer costs by caching content closer to end-users.
(Source: Amazon Web Services, aws.amazon.com)
2. Leverage VPC Endpoints
VPC endpoints can help reduce data transfer fees by keeping traffic within the AWS network.
3. Choose Regions Wisely
Selecting the right AWS region can significantly impact your data transfer costs.
4. Implement Data Compression
Compressing data before transfer can reduce the amount of data moved, lowering costs.
AWS Data Transfer Pricing for Specific Services
Different AWS services may have unique data transfer fee structures. Let’s explore some common services.
Amazon S3 Data Transfer Charges
Amazon S3 follows the standard AWS data transfer pricing model. However, it offers features like S3 Transfer Acceleration for faster transfers at an additional cost.
EC2 Data Transfer Fees
EC2 instances incur data transfer charges for outbound traffic to the internet and between regions. Inbound traffic and traffic between EC2 instances in the same region are generally free.
Note:
Learn more about EC2 instances in our other article Exploring the Fundamentals of Amazon EC2 Instances.
Monitoring and Managing AWS Data Transfer Costs
To keep your AWS data transfer charges in check, it’s crucial to monitor and manage your usage effectively.
Tools for Cost Management
- AWS Cost Explorer
- AWS Trusted Advisor
- AWS Budgets
- Third-party cost management tools
(Source: AWS Blog, aws.amazon.com/blogs)
Regular monitoring helps identify cost-saving opportunities and prevents bill shock.
Common Misconceptions About AWS Data Transfer Pricing
Many users misunderstand certain aspects of AWS data transfer fees. Let’s clarify some common misconceptions:
All Data Transfer is Charged Fact
Inbound data transfer and many types of internal transfers are free. AWS typically doesn’t charge for data transferred into their services from the internet. This policy encourages users to upload data to AWS platforms.
Data Transfer Pricing is Uniform Across All Services Fact
Some services have specific data transfer pricing models that differ from the standard AWS pricing. For instance, Amazon CloudFront has its pricing structure for content delivery.
It’s Always Cheaper to Use a Single Region Fact
While using a single region can reduce inter-region transfer costs, it may not always be the most cost-effective or performant solution. Multi-region architectures can improve latency and provide better disaster recovery options.
Free Tier Covers All Data Transfer Fact
While AWS offers some free data transfer as part of its Free Tier, this is limited and doesn’t cover all types of data transfer. It’s important to understand these limits to avoid unexpected charges.
Understanding these realities behind common misconceptions is crucial for effective AWS cost management and architectural planning.
(Source: Amazon Web Services, aws.amazon.com)
Future Trends in AWS Data Transfer Charges
As cloud computing evolves, so does AWS’s pricing structure. Stay informed about these trends to plan your cloud strategy effectively:
Increased Focus on Edge Computing
With the growing importance of edge computing, AWS may introduce new pricing models for data transfer between edge locations and central regions. This could potentially reduce costs for users with distributed architectures.
More Granular Pricing Tiers
AWS might introduce more nuanced pricing tiers to better accommodate different usage patterns. This could benefit users by allowing for more precise cost optimization.
Enhanced Tools for Predicting and Optimizing Data Transfer Costs
AWS is likely to develop more sophisticated tools for monitoring, predicting, and optimizing data transfer costs. These tools could help users make more informed decisions about their data transfer strategies.
Integration with Machine Learning Services
As AI and ML become more prevalent, AWS might introduce special pricing for data transfer related to these services, potentially offering cost benefits for users leveraging these technologies.
Sustainability-Focused Pricing
With increasing emphasis on environmental sustainability, AWS might introduce pricing incentives for data transfer patterns that are more energy-efficient or align with green computing principles.
Customized Pricing Plans
AWS may offer more personalized pricing plans based on individual usage patterns, allowing for better cost management for businesses with unique data transfer needs.
Staying informed about these potential developments will help you adapt your AWS usage strategy to optimize costs and take advantage of new opportunities as they arise.
Case Study: Optimizing AWS Data Transfer Costs
Let’s examine how a hypothetical company reduced its AWS data transfer charges through strategic planning.
Company X’s Cost Reduction Strategy
- Implemented Amazon CloudFront for content delivery
- Optimized data storage locations
- Used AWS Direct Connect for large data transfers
- Implemented data compression techniques
Result: 30% reduction in monthly AWS data transfer fees.
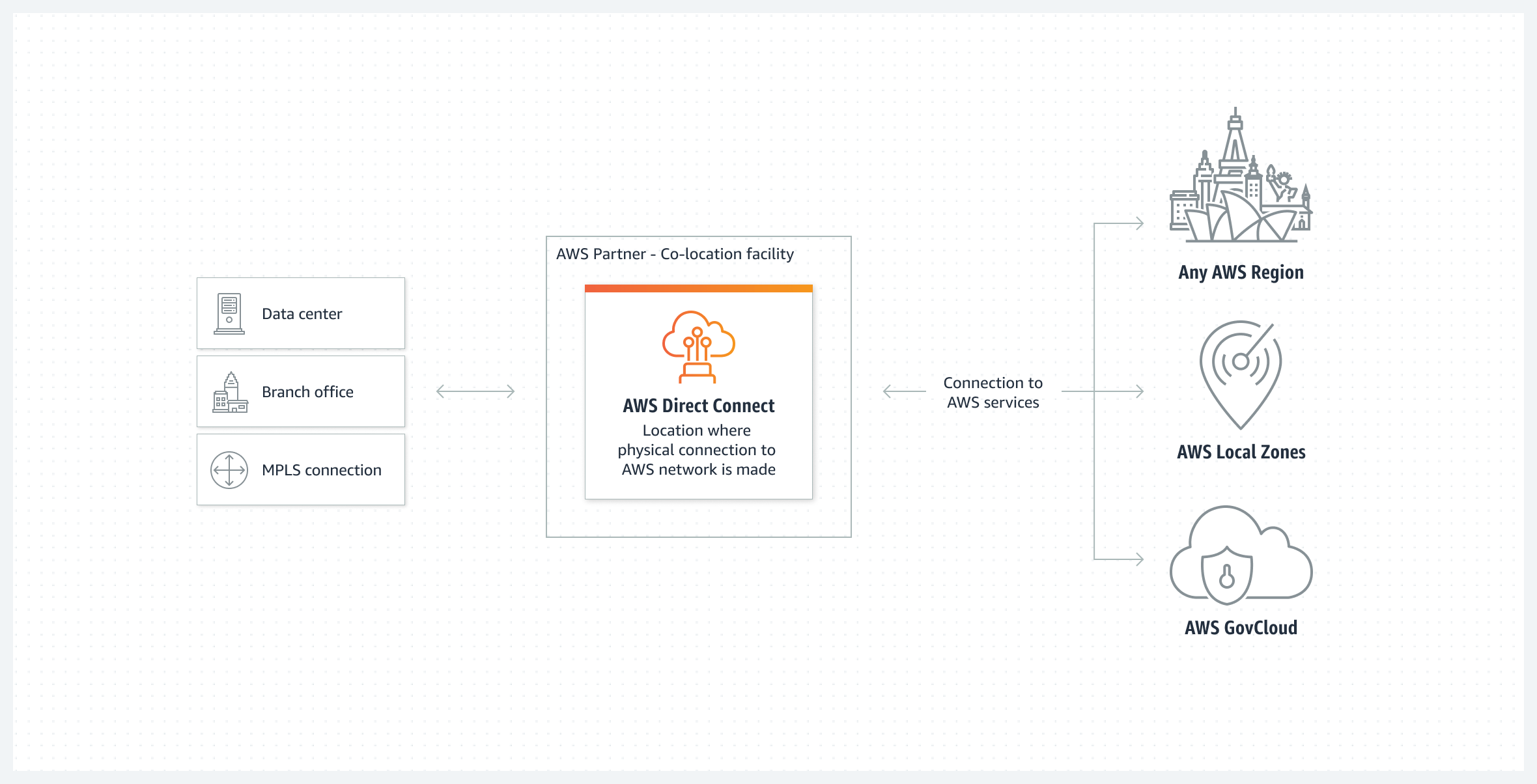
(Source: Amazon Web Services, aws.amazon.com)
Conclusion
As we’ve explored throughout this article, AWS data transfer charges are a multifaceted aspect of cloud computing that requires careful consideration and management. From understanding the basics of inbound and outbound transfers to navigating the complexities of inter-region data movement, mastering these concepts is crucial for optimizing your AWS costs.
Remember, effective management of AWS data transfer pricing isn’t a one-time task but an ongoing process. It requires regular monitoring, a willingness to adapt to new technologies and pricing models, and a strategic approach to your overall cloud architecture. By implementing the strategies discussed – such as leveraging CloudFront for content delivery, using VPC endpoints, and choosing your regions wisely – you can significantly reduce your data transfer costs without compromising on performance or functionality.
As the cloud landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about future trends in AWS pricing and new optimization tools will be key to maintaining a cost-effective cloud strategy. Keep exploring, keep learning, and don’t hesitate to experiment with different approaches to find what works best for your specific use case.
By mastering AWS data transfer charges, you’re not just saving money – you’re positioning your organization to make the most of what cloud computing has to offer, driving innovation and growth in an increasingly digital world. Understanding and optimizing your AWS data transfer fees is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and adaptability to changes in AWS data transfer pricing.If you’re interested in Amazon cloud technologies, read our article Getting Started with AWS Auto Scaling Groups.

